SVP recognizes the previously mentioned wave forms but not as a priori or causitive factors but as measurements of effects or that which is thought to be observed. Earlier work on the SVP view and model can be studied in The Physics of Love - The Ultimate Universal Laws.
In the SVP view a wave is more complex than the overly simplified conventional understanding. The SVP wave model is composed of several seemingly discrete and non-observable parts or functions acting as one composite complex whole.
Wave: A wave is a highly complex continuous reciprocating interchange from one primary state or condition to a seemingly opposite state or condition.
These alternately seemingly opposite phases are a reciprocating interchange (one becoming the other) between integration and disintegration. In short a wave is a periodic change from a state or condition of Harmony (attraction/contraction) to a state or condition of discord (repulsion/expansion). This periodic change of state is caused by and is the effect of the contained relative and proportional values of the individual aliquot parts (frequencies) of the vibrating or oscillating body or aggregate. See Law of Assimilation, Wave Field, Rhythmic Balanced Interchange
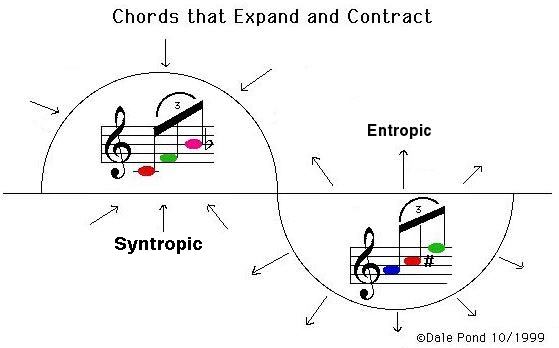
Figure 8.7 - Varying Degrees of Chordal Harmony/Discord Create Varying Degrees of Attraction and/or Repulsion
A vibration is the complex motions and states associated with internal rotation, spin and associated rhythmic changes of state. In this discussion vibration is the same as spin or rotation.
An oscillation is the complex motions and states associated with external revolution and associated rhythmic changes of state. In this discussion oscillation is the same as orbit or revolution.
These two changes of state are dual in nature. For each of these two motions there is its reciprocal. An increase in one is a decrease in the other - always reciprocating. As frequency, for instance increases wavelength decreases. This reciprocating attribute is axiomatic. There are several of these reciprocating attributes or aspects that occur concurrently, phasing in and out of each other during the completion of a wave cycle. A wave then is the combination of all of these interchanges happening all at once, concurrently.
Perhaps the easiest way to visualize this complex interchange is to conceive of a primary duality as a planet in elliptical orbit or revolution about a center, its primary point of focus. This orbital revolution should be seen as two distinct condition changes completing a single orbit. At its point of furthest distance the planet is orbiting at its fastest speed and spinning at its slowest speed. At its point of closest approximation the planet is orbiting at its slowest speed and spinning at fastest speed. Russell refers to this complex change of state as winding speed into power and unwinding power into inertia.
All particles, in whatever vibrating or oscillating medium, are performing the exact same polar interchanges however their rates of interchange may differ. These swappings of speed for power are not the only interchanges. Below is a list of dual experiences, states or conditions (synonyms). All of which are periodic and reciprocal interchanges. Some of these are from Russell's out-of-print book Genero-Radiative Concept (also The Universal One) and a few synonyms I've added in that reflect more of Keely's vocabulary.
| Gravitation | Radiation |
| Centralizing | Decentralizing |
| Center seeking | Center fleeing |
| Concordant | Discordant |
| Harmonic | Enharmonic |
| Assimilation | Dispersion |
| Tight | Loose |
| Polar | Depolar |
| Male | Female |
| Red | Blue |
| Attractive | Repulsive |
| Terrestrial | Celestial |
| Earth | Heaven |
| Order | Chaos |
| Association | Dissociation |
| Appearance | Disappearance |
| Positive | Negative |
| Negative (Keely) | Positive (Keely) |
| Decreasing volume | Increasing volume |
| Generating | Degenerating |
| Inhalation | Exhalation |
| Genero-active | Radio-active |
| Endothermic | Exothermic |
| Integrating | Disintegrating |
| Distinctness | Nebulousness |
| Composing | Decomposing |
| Induction | Conduction |
| Accumulating | Dissipating |
| Charging | Discharging |
| Assembling | Distributing |
| Attracting | Repulsing |
| Absorbing | Emanating |
| High melting point | Low melting point |
| Contracting | Expanding |
| Rising potential | Lowering potential |
| Condensation | Ionization |
| Cooling | Heating |
| High pressure | Low pressure |
| Centripetal | Centrifugal |
| Plus | Minus |
| Freezing | Melting |
| Hardness | Softness |
| Solidity | Tenuity |
| Slow rotation (spin) | Fast rotation (spin) |
| Slow spin | Fast spin |
| Fast revolution | Slow revolution |
| Fast orbit | Slow orbit |
| Density | Evaporization |
| Massive | Tenuous |
| Storing | Leaking |
| Solution | Dissolution |
| Affinity | Disunity |
| Sympathetic | Anti-sympathetic |
| Point |
Circumference |
| Life |
Death |
| Health |
Disease |
Figure 8.8 - Water Wave Model - Polar States or Conditions as Seeming Opposites
See Also
Dynaspheric Force
Father-Mother Principle
Law of Assimilation
Rhythmic Balanced Interchange
Wave Field
