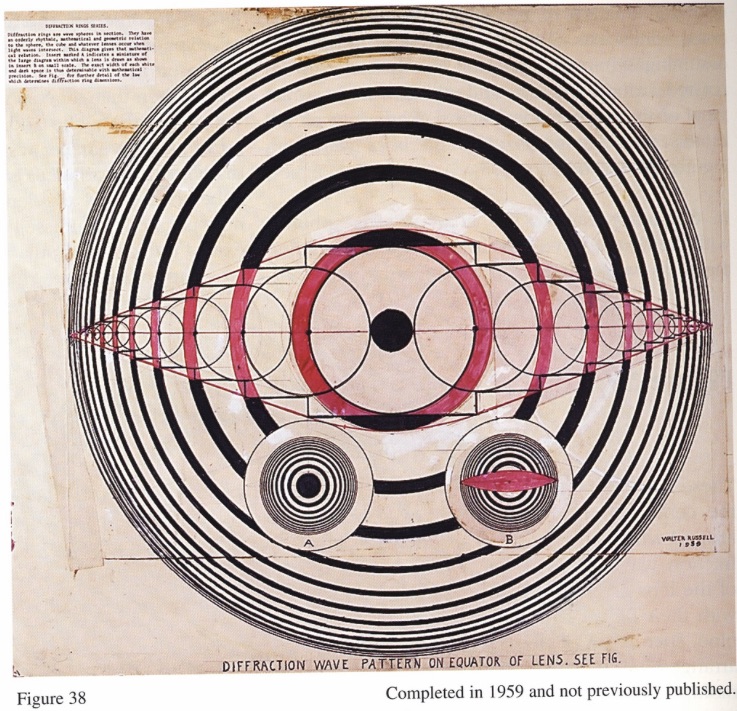
“Diffraction rings are wave spheres in sections. They have an orderly rhythmic, mathematical and geometric relation to the sphere, the cube and whatever lenses occur when light waves interact. This diagram gives that mathematical relation. Sphere marked A indicates a miniature of the large diagram within which a lens is drawn as shown in sphere B as small scale. The exact width of each white and dark space is thus determinable with mathematical precision.” [Dr. Walter Russell]
(courtesy University of Science and Philosophy) (click to enlarge)
See Also
amplitude of the wave amplitude wave position antiwave atmosphere bidirectional wave pair biosphere Book 02 - Chapter 16 - Expressions of Gravitation and Radiation - The Wave Brain Waves carbon octave wave Chapter XII - Mental Atmosphere Chladni wave plate Compression Wave Compression Wave Velocity concentric waves of attraction convert frequency to wavelength convert wavelength to frequency Cosmic microwave background Cube Sphere cube wave cube wave-field cube wave-field of zero curvature cube-sphere Cubing the Sphere Curved Wave Universe of Motion Debye Sphere disintegratory sphere Dissociating Water with Microwave Dynasphere Dynasphere Applications Dynasphere Construction Dynasphere Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Frequency Response Profile - A Novel Experiment Dynaspheres to Europe Project Dynaspheres to Japan Dynaspheres to the World electric thought-wave electric wave electrogravitational wave electromagnetic sound wave ethereal atmosphere Etheric Liberator used with Atlin the Musical Dynasphere etheric wave motion Figure 12.10 - Russells Locked Potential Wave Figure 12.12 - Russells Multiple Octave Waves as Fibonacci Spirals Figure 12.12 - Russells Multiple Octave Waves as Fibonacci Spirals - See Also Figure 13.02c - Dynasphere Neutral Center Figure 13.09 - Primary Emanations from within Dynaspheres Figure 13.11 - Russells Ring of Motion Superimposed on Dynasphere Profile Figure 13.13 - Gravity Syntropic and Radiative Entropic Waves Figure 13.13 - Gravity Syntropic and Radiative Entropic Waves - See Also Figure 14.07 - Love Principle: Two sympathetic waves expanding from two points have one coincident centering locus Figure 16.02 - Electricity Evolves Mass into Spheres Figure 19.01 - Keely and his original Dynasphere Figure 19.02 - Dale Pond and his replica of Keelys Dynasphere Figure 19.04 - Dynasphere Components Figure 19.06 - Inside view of Keelys original Dynasphere Figure 2.1.5 - Russells Rings forming Spheres from Three Pairs of Reflecting Mirrors Figure 20.01 - Keely and his original Dynasphere circa 1889 Figure 20.02 - Dale Pond and his replica of Keelys Dynasphere 1996 Figure 20.04 - Dynasphere Components Figure 20.15 - Dynaspheres Across America Figure 3.26 - Formation of Spheres along Six Vectors of Cubes Figure 4.11 - Six Planes and Three Shafts Coincide to Produce Spheres Figure 5.1 - Swirling Vapor in the Atmosphere Figure 5.4 - Vortex and Gyroscopic Motion on One Plane then on three forming Sphere Figure 6.10 - Wave Dynamics between Cube Corners Figure 6.12 - Spheres and Cubes are Gods Only Tools Figure 6.18 - Sphere Circumscribed by Cube Figure 6.19 - Sphere to Cube - Relations and Proportions Figure 6.9 - Russell depicts his waves in two ways Figure 7.1 - Step 1 - Wave Vortex Crests at Maximum Polarization Figure 7.3 - Step 3 - Sphere Forms Orthogonally Triple Compressing Shell Layers Figure 8.1 - Russells Painting of Wave Form Dynamics Figure 8.10 - Each Phase of a Wave as Discrete Steps Figure 8.11 - Four Fundamental Phases of a Wave Figure 8.14 - Some Basic Waveforms and their constituent Aliquot Parts Figure 8.2 - Compression Wave Phase Illustration Figure 8.3 - Coiled Spring showing Longitudinal Wave Figure 8.4 - Transverse Wave Figure 9.10 - Phases of a Wave as series of Expansions and Contractions Figure 9.11 - Compression Wave with expanded and contracted Orbits Figure 9.13 - Wave Flow as function of Periodic Attraction and Dispersion Figure 9.14 - Wave Flow and Phase as function of Particle Rotation Figure 9.15 - Wave Flow and Wave Length as function of Particle Oscillatory Rotation Figure 9.5 - Phases of a Wave as series of Expansions and Contractions Figure 9.9 - Wave Disturbance from 0 Center to 0 Center forward-time wave Frequency Wavelength Light Energy gradient wave harmony of the spheres Hemispheres hot sphere of matter HOW THE MUSICAL SPHERE ROTATES In the Wave lies the Secret of Creation isochronous wave Keely Sphere Was No Secret Keely WaveFunction Kepler Music of the Spheres Kinetic Alfven Waves light as wave and particle light wave light waves in motion light-wave Longitudinal Wave Longitudinal Waves in Vacuum Love wave master key of wave mechanics and space geometry Matter Waves and Electricity Microwave microwave oven Music of the Spheres Musical Dynasphere musical sphere Nodal Waves Noosphere octave wave octave wave shaft octave wave tones octave wave-field principle One More Step Toward Building The Cube-Sphere Wave-Field Part 05 - Three Rotating Planes Become Spheres Part 19 - Musical Dynasphere - Historical Part 20 - Musical Dynasphere - Current Research phase conjugate gradient wave phase conjugate replica wave phase-locked time-forward electromagnetic wave phase-locked time-reversed electromagnetic wave PHILOSOPHY OF TRANSMISSION AND ROTATION OF MUSICAL SPHERE Pulsing Electric Thought-Waves Radio Waves Rayleigh Wave resonating sphere REVOLVING SPHERE ROTATED BY VIBRATIONS Russell Wavefunction Russell Wavefunction Equation seed of the octave wave Shock Wave sine wave sphere sphere is a compressed cube sphere motor sphere of activity SPHERE RESONANCE sphere-interrupter spinning sphere Standing Wave Standing Waves stress potential wave Table 12.02.01 - Wavelengths and Frequencies The Wave - page 180 The Wave - Page 181 The Wave - page 182 The Wave - page 183 The Wave - page 184-185 The Wave - page 186 thought wave thought wave amplitude Thoughtsphere Three Main Parts of a Wave time-reversed replica wave tonal nature of octave waves tonal wave position Transverse Wave universal wave vacuum electromagnetic wave wave wave amplitude wave axis wave current wave cycle wave cycle - See Also Wave Field Wave Fields - Summarize and Simplify wave fulcrum wave number wave octave formula wave of gravity control wave pair wave plate wave shaft wave train wave unit wave-crest tone wave-field wave-field projector wave-lever waveform wavefunction waveguide WaveLength We Now Build the Nine Equators of Cube-Sphere Wave-Fields What is a Dynasphere 12.05 - Three Main Parts of a Wave 13.09 - Sphere Rotated by Vibrations 16.06 - Electric Waves are Sound Waves 19.03 - Philosophy of Transmission and Rotation of Musical Sphere 19.05 - Excerpts from original Articles about Keelys Globe Motor or Musical Sphere 2.1 - Rings and Spheres 20.02 - Keely Describing Dynasphere Construction 3.8 - There are no Waves 3.9 - Nodes Travel Faster Than Waves or Light 5.6 - Vortex Forming Spheres 6.14 - Sphere and Cube 8.3 - Conventional View of Wave Motion 8.4 - Wave types and metaphors 8.5 - Wave Motion Observables 8.6 - Wave Form Components 8.8 - Water Wave Model 9.2 - Wave Velocity Propagation Questions 9.30 - Eighteen Attributes of a Wave 9.31 - Oscillatory Motion creating Waveforms 9.34 - Wave Propagation 9.35 - Wave Flow
