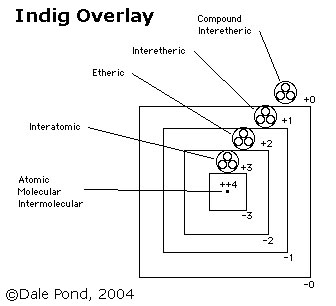
Vacuum or dispersed matter at 0 - greatest volume.
Matter or condensed etheric substance (scalar or mind) at 4+, least volume.
[see 7.6 - Reciprocal Disintegration and Creation, constant of proportionality]
See Also
12.01 - Scale of Locked Potentials
12.04 - Locked Potentials and the Square Law
12.27 - Potentials
15.23 - Water is Predominantly Diamagnetic
16.13 - Differential Densities
2.7 - Differential Densities
3.22 - Quantum Leap Delta equivalent to Locked Potentials Delta
6.13 - Density Differentiation
7.6 - Reciprocal Disintegration and Creation
9.36 - Law of Matter and Energy
Apparatus For Producing Electric Currents of High Frequency and Potential - 568176
bias
Chart of Locked Potentials - See Also
Chart of Locked Potentials
Chart of Matter and Energy
cold multiplies electric potential
Compound Interetheric
constant of proportionality
counter-reactive transverse electrical potentials
coupled potential gradient
CURRENT-FREE POTENTIAL
curvature of electric potential pressure
depotentialization
differential densities
Dimension
electric potential difference
electric potential
electromagnetic potential
electrostatic potential difference
electrostatic scalar potential
Entropy
Equilibrium
equipotential environments
equipotential level
Ether
Etheric Elements
Euler Lagrange Equation
fast motion multiplies electric potential
Figure 12.04 - Locked Potential Points Relations and Descriptions
Figure 12.10 - Russells Locked Potential Wave
Figure 12.11 - Russells Locked Potential Full Ten Octave Gamut
Figure 3.13 - Orthogonal Vector Potentials
Figure 3.5 - Conflicting and Opposing Vector Potentials
Figure 9.12 - Scale of Locked Potentials over Time
heat divides electric potential
Impedance
inner potential
Interetheric
Latency
Latent
List of Synonyms for Scalar
Locked Potentials and Subdivisions
Locked Potentials and the Square Law
longitudinal magnetic potentials
magnetostatic scalar potential
Mind Force
Mind
multiplication of electric potential
negative
negatively potentiated ray-form
negatively potentiated
omni-Magnetic-potential
Part 12 - Russells Locked Potentials
positive
potential density
Potential gradient
potential hydrogen - pH
Potential
Potential
potential-less
potentialization
potentialize
potentiate
potentiation
Potentiometer
predominant
predominantly centrifugal
predominantly centripetally
Predominantly Entropy
predominantly magnetic
predominantly positive potentialities
Predominantly Syntropy
rings of electric potential
scalar electromagnetic potential
Scalar Potential
Scalar
Scale of Locked Potentials
stress potential wave
Subdivision
Syntropy
Table of Cause and Effect Dualities
The Seven Subdivisions of Matter and Energy
Universal Heart Beat
Vector Potential
zero electric potential
zero potential holes
