The Schumann resonances (SR) are a set of spectrum peaks in the extremely low frequency (ELF) portion of the Earth's electromagnetic field spectrum. Schumann resonances are global electromagnetic resonances, excited by lightning discharges in the cavity formed by the Earth's surface and the ionosphere.
This global electromagnetic resonance phenomenon is named after physicist Winfried Otto Schumann who predicted it mathematically in 1952. Schumann resonances occur because the space between the surface of the Earth and the conductive ionosphere acts as a closed waveguide. The limited dimensions of the Earth cause this waveguide to act as a resonant cavity for electromagnetic waves in the ELF band. The cavity is naturally excited by electric currents in lightning. Schumann resonances are the principal background in the electromagnetic spectrum beginning at 3 Hz and extend to 60 Hz, and appear as distinct peaks at extremely low frequencies (ELF) around 7.83 (fundamental), 14.3, 20.8, 27.3 and 33.8 Hz.
In the normal mode descriptions of Schumann resonances, the fundamental mode is a standing wave in the Earth-ionosphere cavity with a wavelength equal to the circumference of the Earth. This lowest-frequency (and highest-intensity) mode of the Schumann resonance occurs at a frequency of approximately 7.83 Hz, but this frequency can vary slightly from a variety of factors, such as solar-induced perturbations to the ionosphere, which comprises the upper wall of the closed cavity. The higher resonance modes are spaced at approximately 6.5 Hz intervals, a characteristic attributed to the atmosphere's spherical geometry. The peaks exhibit a spectral width of approximately 20% on account of the damping of the respective modes in the dissipative cavity. The eighth overtone lies at approximately 59.9 Hz. Wikipedia, Schumann Resonances
The Static from the television.
In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson published a scientific study which proved that a radio signal with a wavelength of 7.3 cm was being emitted uniformly throughout all parts of the sky. This signal became known as cosmic microwave background radiation. Penzias and Wilson won the Nobel Prize in physics in 1978 for their findings. It is believed that this cosmic static is comprised of photons of energy that are still cooling 15 billion years after the Big Bang. If you turn a television to a channel with no station, you will see this static and given the level of intelligence of most TV programs, this static is about the only thing worth watching. [unknown source]
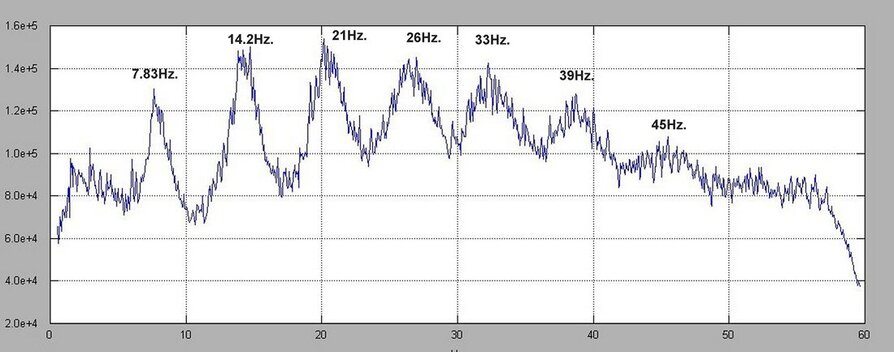
There are SEVEN Schumann Resonances. NOT just one. All are at different frequencies. 7.83Hz. is the 1st. then the 2nd. at 14.2Hz. then the 3rd. at 21Hz. then the 4th. at 26Hz. then the 5th. at 31Hz. to 33Hz. then the 6th. at 39Hz. and then the 7th. at 45Hz. They are NOT Harmonics of the first resonance at 7.83Hz. They are all Mathematically related to each other but they ARE NOT Harmonics. [Benjamin Lonetree]
See Also
